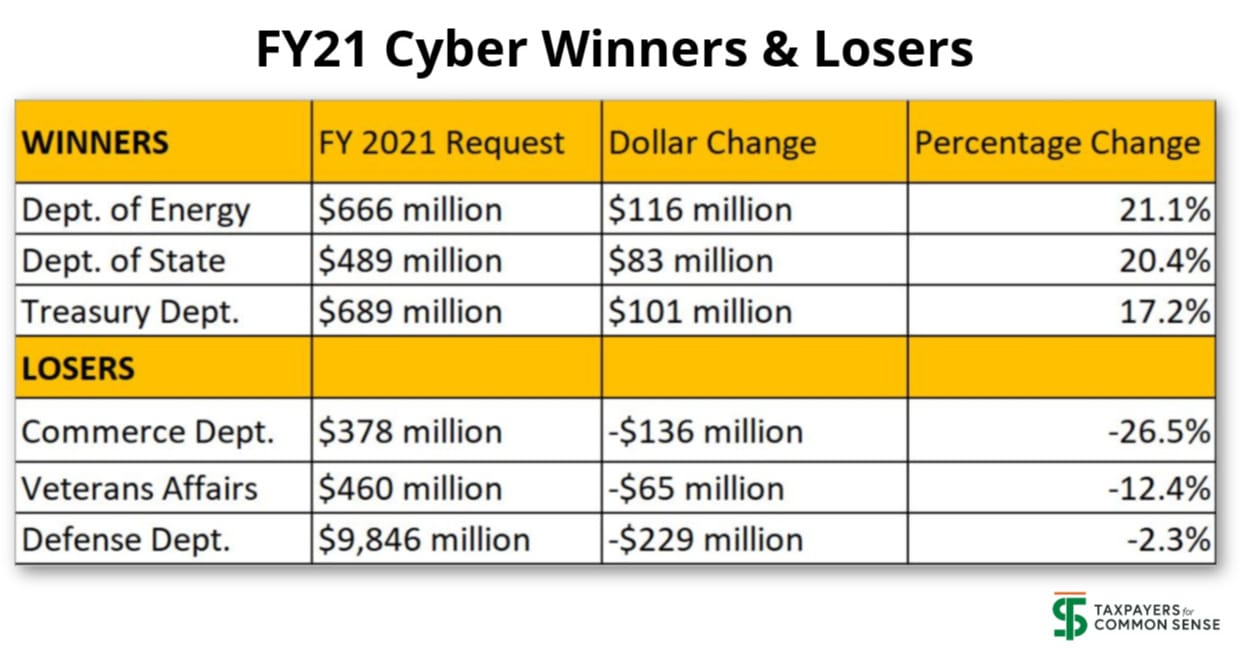
President Trump’s FY21 budget request includes $18.77 billion for cybersecurity-related activities of the federal government, a $13 million decrease (about 0.1 percent) below the FY20 levels. Because some cybersecurity funding is classified, this amount does not represent the entire U.S. cybersecurity budget.
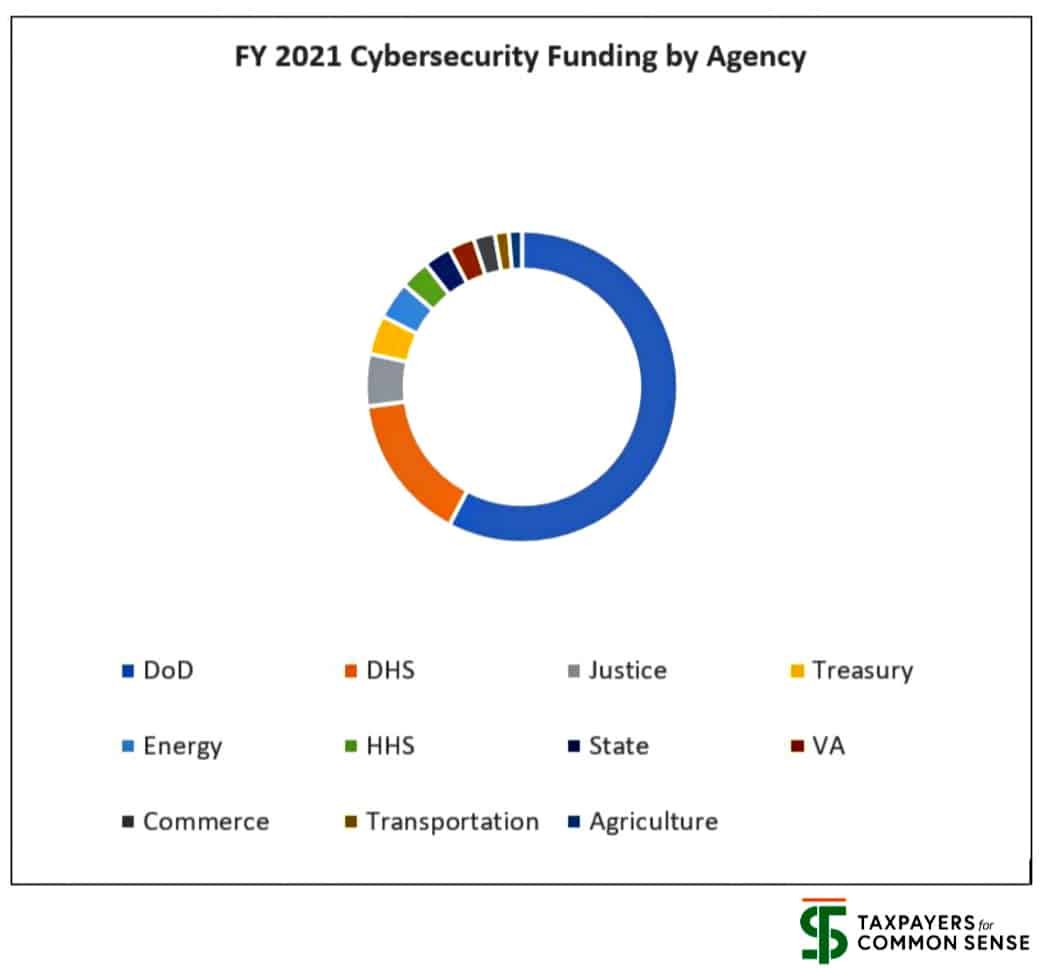
The Defense Department makes up the largest share of the total cybersecurity spending, at $9.8 billion accounting for more than 52 percent in this year’s budget. This funding includes such things as the Pentagon’s efforts to defeat enemy cyber attacks against U.S. forces and the military’s abilities to conduct cyber warfare against existing and potential adversaries.
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) cybersecurity budget is a distant second at $2.6 billion. DHS is the lead federal agency charged with securing the federal government’s civilian information technology (IT) systems against cybersecurity attacks and sharing cybersecurity information with state and local governments. The DHS cybersecurity FY21 budget request is about $30 million above current levels (1.2 percent increase).
There were a number of significant winners and losers among the federal agencies with the largest cybersecurity budgets (click to zoom in on chart below):
The FY21 DHS request also marks the second year of funding for the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), which was created from the former National Protection and Programs Directorate (NPPD) in November 2018. CISA coordinates across all levels of government and with the private sector to protect the nation’s critical infrastructure from physical and cyber threats. The request includes $1.8 billion for CISA in FY20, a decrease of roughly $254 million from FY20 (14 percent decrease).
The following pie chart (click to zoom in) provides a basic breakout of the major areas of total federal cybersecurity spending.











Get Social